Changing How Medicine Is Practiced
Technology has influenced medicine in a major way. New types of artificial intelligence aid in diagnosing and treating conditions, and the rise of telehealth makes medical care more accessible and convenient. One less appreciated field, however, is having a major impact on how medicine is practiced today: Robotics. Here are some of the ways medical robots are improving how medicine is practiced today and how this field is expected to evolve over time.
Robotic Prosthetics
Prosthetics are perhaps the area where robotics is the most natural fit. Many robots, after all, have limbs that operate similarly to their human counterparts, and bringing these capabilities to people makes sense.
Challenges remain, however. While robotic devices can meet or even exceed the capabilities of human limbs, letting their users operate them in a seamless manner remains unsolved. Fortunately, advances in neurological science offer good reason for optimism that this gap can be bridged in the foreseeable future, and devices are already on the market today. However, the high cost involved in purchasing and maintaining these devices means they remain unaffordable for many people who could benefit.
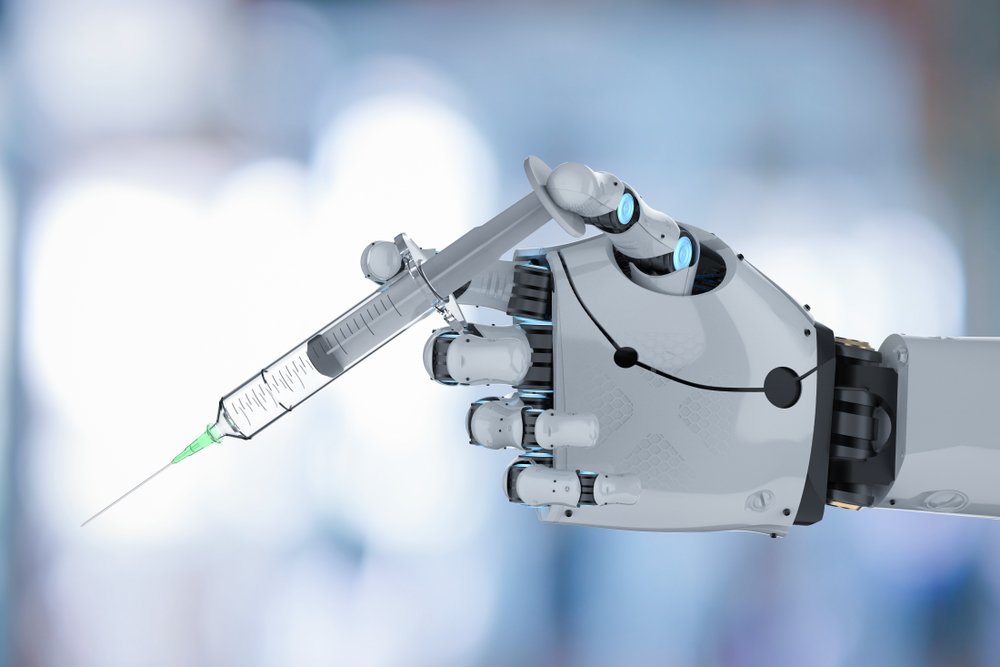
Robot-Assisted Surgery
Surgeons have a remarkable ability to perform fine work, but even the steadiest of human hands cannot match the precision of modern robots. In addition, robots are not bound by human anatomy; potential surgical techniques have often been left unexplored because humans simply cannot perform the physical actions required. Today, most robotics used in surgery are used as assistants, allowing human surgeons to work with them in tandem. By automating certain tasks, robots can reduce the mental load demanded by surgery, potentially reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
Better optical capabilities have also allowed robotic surgeons to operate in areas previously handled exclusively by people. Although it will be some time before your human surgeon is fully supplanted by a robot, the trend is clear.
Social Robots
Mental health is a critical part of overall health, but many people, especially the elderly, often find themselves lacking supportive companionship. Isolation has been linked to a number of physical medical problems, and lacking a social support network can exacerbate or even cause depression. While online contact can be beneficial, it lacks the tangible components of human interaction.
A significant amount of research has focused on using robots as an alternative means of socialization. Although those who interact with robots know they aren’t speaking with a real human, studies still show positive benefits. Furthermore, advances in robotics and the software that powers them can make interactions more similar to real-world interactions with humans. Ethical questions still remain, but robots can help people maintain better mental health by providing positive, supportive interactions.
Physical Therapy Robotics
Physical therapy is invaluable for many people recovering from surgery or other medical events, and it can help those with ongoing conditions interact with the world more seamlessly. Already, physical therapy depends on both humans and machines to work effectively; devices that help support a person relearning to walk on a treadmill, for example, are essential. By adding robotic capabilities to devices, physical therapists can offer a broader range of therapies.
Additionally, physical therapy often involves repetition, and the need for a physical therapist to be present means patients might not receive the maximally beneficial volume of therapy. By relying on robots during repetitive tasks, physical therapists can potentially treat multiple patients simultaneously, bringing down the cost of care. Furthermore, some physical therapy robots can be used at home, providing convenience and allowing patients to perform lengthier sessions than are practical in a medical facility.
Hospital Support Robots
Hospitals and other medical centers demand a significant amount of work. In particular, sanitation is a major concern in hospitals, as hospital-acquired infections are far more common than many realize and are often difficult to treat as bacteria becomes more resistant to available antibiotics. Although janitors and other support staff often do an excellent job at keeping hospitals clean, small mistakes and a lack of sufficient staff can increase the odds of patients developing problems. With sterilizing and cleaning robots, hospitals can help prevent avoidable infections.
In addition, it’s often up to nurses and other staff to deliver medicine to patients and complete other routine tasks. These types of activities are great to offload to mobile robots, allowing staff to focus on tasks that robots can’t yet perform. Although such robots are expensive, they can ultimately let hospitals operate more efficiently, lowering the cost of medical care.
Laboratory Robots
Many advances in medicine began in labs performing basic science research and testing potential pharmacological applications. This research, often performed on mice and other animals, is typically time-consuming and repetitive. By utilizing robots designed to perform these tasks, people working in laboratories can spend their time on more important tasks, potentially making it easier to discover and test new therapies.
Additionally, working in a laboratory can be dangerous, as accidental exposure to medicines and other chemicals can have disastrous results. Robots, however, are immune to these risks, making them ideal candidates for certain types of work. In addition, they can often operate more precisely than even the most experienced lab technicians, allowing researchers to capture better data. Robots can operate at all hours, letter labs generate their results in a more timely manner.
Telepresence Robots
Telehealth is a rapidly growing field. Although doctors can offer a broad range of services remotely, many tasks can only be performed in person. By simply relying on a device that allows a doctor to move a camera around a patient’s body, telepresence robots can potentially expand the scope of telehealth, letting them help their patients regardless of their location.
Telepresence robots can also be used on site. Robots that can operate a camera through a small surgical cut, for example, enable doctors to perform surgery in a much less invasive manner, improving recovery times for patients and reducing the odds of negative outcomes. Much like surgical robots, telepresence robots can serve as useful assistants, capable of performing tasks impossible for humans.